The amount of psi can also be calculated from the amount of the milliamp signal, or one can calculate the amount of the milliamp signal when the amount of psi is known. Each of these signals has an offset and a span that must be taken into account for the calculation.
The offset for the milliamp signal is 4 mA, and the span is 16 mA. The span is determined by subtracting the lower value from the higher value (20 mA - 4 mA). The offset for the psi signal is 3 psi, and the span is 12 psi (15 psi - 3 psi).
The formula for converting between these two systems is shown in the following equation. The milliamp signal is identified as A1 and the pressure signal is identified as P1.
When one is converting from one to the other, either P1 or A1 will become a known value in the formula. The value 4 in the left side of the equation represents the 4 mA offset, and the value 16 represents the 16 mA span. The value 3 in the right side of the formula represents the pressure offset, and the value 12 represents the 12 psi span…
(A1 - 4)/16 = (P1 - 3)/12
The formula can be further simplified in terms of an unknown pressure or an unknown milliamp signal. The following equations show these two simplifications.
P1 = ((A1 - 4)/16) x (12) + 3
Or
A1 = ((P1 - 3)/12) x (16) + 4
Exercise
Use the graph in this graph or the formula to determine the amount of air pressure that one would expect to find at the valve for the following electrical signals: 4 mA, 8 mA, 12 mA, 17.5 mA, and 20 mA.
One needs to know these values if one is troubleshooting the valve and amplifier, or if one were trying to complete a field calibration to ensure the valve moved its full range 0-100% as it received the electrical signal.
Solution
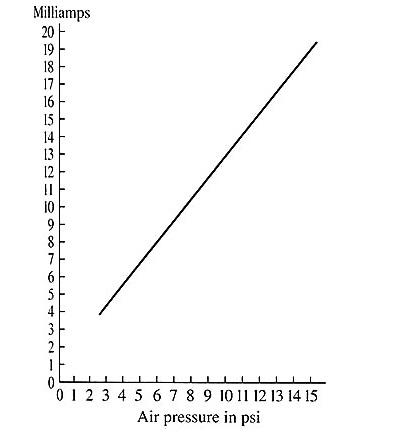
The graph shows that the air pressure ranges from 3-15 psi and the electrical signal ranges from 4-20 mA. Some of the values that line up on the graph will allow one to use the graph to get accurate conversion.
For instance, the amount of air pressure for a 4 mA signal is 3 psi. The amount of air pressure for 8 mA is 6 psi. The amount of air pressure for 12 mA signal is 9 psi, and the amount of air pressure for the 20 mA signal is 15 psi.
The amount of air pressure for 17.5 mA will not show up accurately on the graph, so one may use the formula to calculate the amount of pressure.
P1 = ((A1 - 4)/16) x (12) + 3
P1 = ((17.5 - 4)/16) x (12) + 3
P1 = 13.125 psi