Client/server network operating systems allow the network to centralize functions and applications in one or more dedicated file servers (See fig. ).
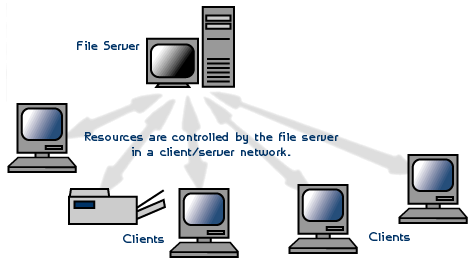
The file servers become the heart of the system, providing access to resources and providing security. Individual workstations (clients) have access to the resources available on the file servers.
The network operating system provides the mechanism to integrate all the components of the network and allow multiple users to simultaneously share the same resources irrespective of physical location. UNIX/Linux and the Microsoft family of Windows Servers are examples of client/server network operating systems.
Advantages of a client/server network:
- Centralized - Resources and data security are controlled through the server.
- Scalability - Any or all elements can be replaced individually as needs increase.
- Flexibility - New technology can be easily integrated into system.
- Interoperability - All components (client/network/server) work together.
- Accessibility - Server can be accessed remotely and across multiple platforms.
Disadvantages of a client/server network:
- Expense - Requires initial investment in dedicated server.
- Maintenance - Large networks will require a staff to ensure efficient operation.
- Dependence - When server goes down, operations will cease across the network.