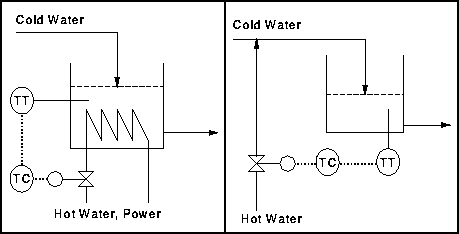
Temperature Control
Components
- Temperature Indicator
- Control Valve
- Temperature Controller
Strategy
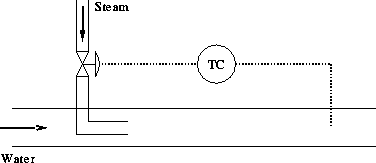
The temperature of the fluid downstream of the valve is regulated using feedback control.
- Measured variable - Temperature of stream
- Manipulated variable - Flowrate of steam
- Disturbances
- Flowrate of water
- Temperature of water
- Temperature of steam
Operation
If the temperature of the stream increases then the valve is closed. If it decreases the valve is opened.
This control system will work regardless of the cause of a change in temperature, which can be brought about by a change water or steam temperature or of water flowrate.
Unlike the previous example it is of course necessary to measure the temperature downstream as this is what is to be regulated!
With any proposed control system simply ask yourself: “Does moving the valve change the measured variable?” If the answer is “No” then the control system cannot work.