Wireless SCADA and How does it work ?
Wireless SCADA is required in those applications when wireline communications to the remote site is prohibitively expensive or it is too time-consuming to construct. In particular types of industry such as Oil & Gas or Water & Wastewater, wireless SCADA is often the only solution due to the remoteness of the sites.
Wireless SCADA systems can be built on a private radio (licensed or unlicensed), cellular or satellite communications; each of these has its own unique set of characteristics as given in the Table below.
One major difference between Private Radio and Cellular or Satellite is that Private radio has no associated monthly fees. Once you build your hardware infrastructure, you own it. With Cellular or Satellite Service providers, there is an associated monthly fee. This is usually $40 Cdn or greater per month depending on the Service Plan.
For the decision maker, it comes down to deciding between a large capital investment and no monthly service fees OR a smaller capital investment with monthly service fees. If the client’s remote assets are well within the Service Providers coverage area, they have high speed or TCP/IP data requirements or their remote sites are there for a short term (lasting no more than 1 or 2 years) all of these factors contribute to making Cellular communications a more attractive option.
If the assets are extremely remote (hundreds or thousands of miles away from civilization) and /or they have TCP/IP LAN speed requirements then Satellite communications is obviously the only solution. Often it is more typical for companies to have a mixture of solutions; using Point-Multipoint Private Radio communications where there is a high density of remote sites served by the one Master site, using Cellular for sites for from Private radio clusters and or satellite for the very remote sites.
Another difference between Private Radio networks and Cellular or Satellite networks is expansion capabilities. With Private Radio systems, if distances between communicating sites are too great for a single hop, then repeaters can always be installed to further the range. This certainly adds to the overall project cost but it is at least an option if required.
With Cellular or Satellite, one is leveraging the vast existing infrastructure of the Service Provider. The advantage of Cellular or Satellite is that the client has access to very wide coverage but the disadvantage is that if there is a site that happens to be outside of the Service Providers coverage, there is no way for the client to increase the range; only the Service Provider can do that.
If Cellular communications make sense as the overall SCADA strategy, it is possible to use Private Radio as “Last Mile Links” to these few remote sites that fall outside of the Cellular coverage maps…. to extend the coverage from the Cellular to a Private network to get to these remote assets.
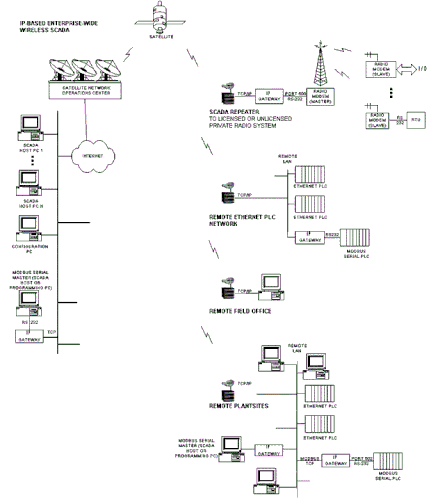
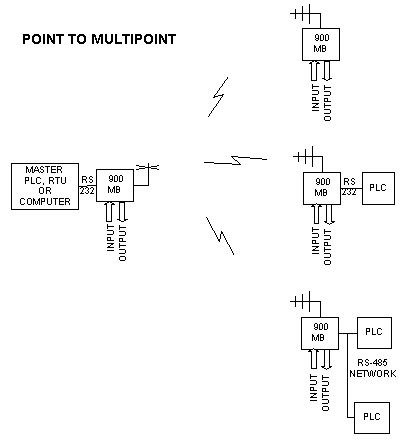
The typical wireless SCADA architecture is Point-Multipoint with one Master polling multiple remote RTU’s (Remote Terminal Units) or PLC’s using RTU or PLC data communication protocols including protocols such as Modbus, AB-DF1, and DNP3.0.
Each PLC or RTU at the remote site is programmed with a unique system address and those addresses are all configured into the SCADA Host MMI. The SCADA Host then polls these addresses and stores the acquired data into its database. It will perform centralized alarm management, data trending, operator display, and control.
Modern SCADA Host MMI’s like NetSCADA can easily accommodate many different types of industrial protocols and the architecture allows multiple clients to view the same data and seamless expansion to handle additional remote sites and i/o points.
Bentek Systems provides complete turnkey SCADA and Wireless SCADA communications solutions from the SCADA Host MMI to the Satellite or Cellular communications or Private Radio communications.
Wireless SCADA systems can range from simple Point-Multipoint systems like the 900-MB Spread Spectrum system below using Modbus protocol:
….to IP-based enterprise-wide systems which use IP protocol to integrate a variety of autonomous communications subsystems:
source - scadalink